Related Products
For Parents
Related Teacher Tools Takeout Items
Checklist for Language of Directions Skill Development
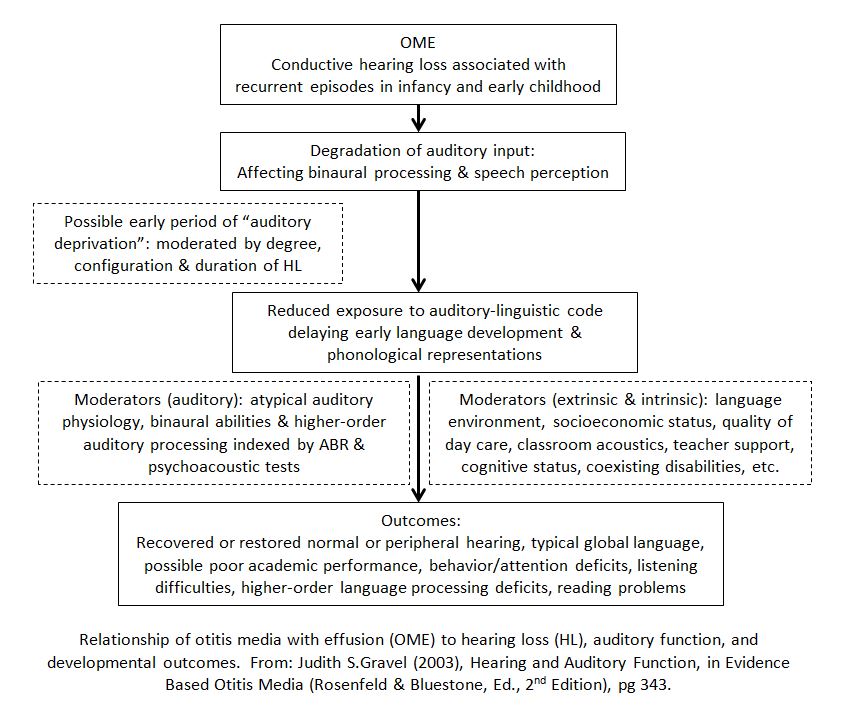
Ear Infections and Learning
My son has had ear infections since he was a tiny infant. Now he doesn’t say his words clearly. Can this be because of the many ear infections he has had?
Information on ear infections:
Hearing Loss Related to Childhood Ear Infections
Download a handout with basic information:
Ear Infections and Early Learning
has information that sheds light on the effects of hearing loss that comes and goes on children’s development.
Ear infections typically cause conductive hearing loss. Refer here for more information about what
conductive hearing loss is and what causes it.
What to watch for as your child learns to talk:
Ear Infections and Language Development
Serious consequences! Ear infections if untreated too long can result in the growth of cholesteatomas. Refer to the webpage on
cholesteatomas for more information about this disease and how it can effect learning. Other
permanent damage can also be caused from longstanding hearing loss due to middle ear infection.
Information you can share with a child’s teacher:
fluctuating hearing loss (ear infections)
Impact of Fluctuating Hearing Loss on Learning
Subtle long-term problems that occur with children who have histories of recurrent ear infections and fluctuating hearing loss include:
- Binaural speech perception deficits, specifically in
spatial listening. - Inability to listen well when there is background noise. It’s harder for them to “target” the sounds they’re supposed to be listening to (result of spatial processing listening deficits).
- Behavior problems may occur because of inattentiveness. They are unable to stay focused on the classroom task at hand.
- Reading difficulties may occur because language is learned through speech. Thus, a child may not be able to read aloud or understand a word beginning or ending in “f,” a sound that is more difficult than others to hear.
- Speech itself sometimes is affected. But most often, that is corrected by school age.
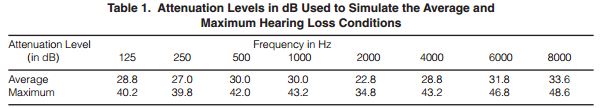
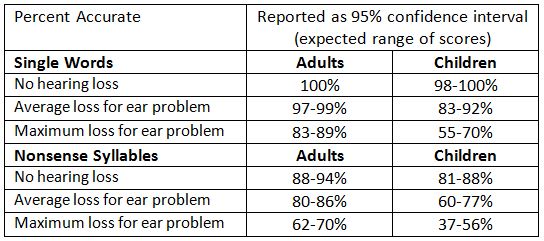
Research Summary: Otitis media with effusion (OME) often results in hearing loss for children with the condition. In order to provide appropriate and effective audiologic management, it is important to understand the impact of OME on speech recognition ability when hearing loss is present. This study examined the speech recognition abilities of normal-hearing six- and seven-year-old children (n = 12) and adults (n = 12) using monosyllabic words and nonsense syllables presented at two levels of simulated conductive hearing loss characteristic of OME. Average speech recognition scores decreased as the degree of simulated conductive hearing loss increased. Both age groups scored significantly poorer for nonsense syllables than for monosyllabic words. In general, the children performed more poorly than the adults with the exception of the easiest listening condition for word stimuli. Furthermore, children appeared less able than adults to use their knowledge of familiar words to improve performance. These findings suggest that rehabilitative strategies may best be focused on combining familiarization techniques and amplification options.